1 Introduction
Zinc sulfide ores are the main source of zmc metal in the world, in which zinc generally exists in forms of sphalerite and marmatite. Currently,more than 80 per cent of the zinc is produced by conventional zinc hydrometallurgical methods, including roasting, leaching and electrowinning processes [1, 2]. % of the zinc is produced by conventional zinc hydrometallurgical methods, including roasting, leaching and electrowinning processes [1, 2]. During the roasting process, ZnS is converted to ZnO, but a significant fraction of ZnO reacts with the iron impurities to form zinc ferrite [3-51]. Zinc ferrite is insoluble in mild acidic conditions, strong Hs. A considerable amount of leaching residue will be produced in the subsequent leaching process [f6, 7]. In addition, the leaching reaction rate decreases over time due to the decreasing acid concentration during the tradifional leaching process in the stirred tank. Consequently, incomplete leaching will OCCur, thereby further increasing the generation of zinc leaching residue (ZLR), leading to a significant waste of resources and a high environmental impact. Consequently, incomplete leaching will OCCur, thereby further increasing the generation of zinc leaching residue (ZLR), leading to a significant waste of resources and a high environmental risk [8, 9]. The high demand for zinc has attracted the interest of industry to utilise the ZLR as a valuable secondary source [1].Hydrometallurgical processes are dely applied to recycle zinc from ZLR due to their significant advantages of lower capital and operating costs, as well as being less harmful to the environment [1, 1]. environment [1, 2]. Currently, the most common hydrometallurgical process is to recover zinc from ZLR in a bath of hot concentrated sulfuric acid [10]. high extraction rate of zinc can be obtained using this process, but incomplete leaching still occurs due to the leaching in the stirred tank.Moreover, the hot concentrated acid leaching process involves a high extraction rate of zinc in a bath of hot concentrated sulfuric acid. Moreover, the hot concentrated acid leaching process involves a long reaction time f4-6¨and consumes an enormous amount of energy and sulfuric acid More importantly, in most electrolytic zinc plants, the ZLRs containing water-soluble zinc with a content of less than 5 per cent of the ZLRs were used to produce the ZLRs in the stirred tank. More importantly,in most electrolytic zinc plants, the ZLRs containing water-soluble zinc with a content of less than 5% are directly discharged or heaped, causing a portion of the zinc losses. The water-soluble zinc can cause soil contamination, water pollution and several other serious environmental pollution through the leachate by rainfall [8, 9]. Therefore, finding a cost effective and environment friendly process to recover zinc from ZLR remains a major challenge. The membrane filter press (MFP), which is a common machine on solid. The membrane filter press (MFP), which is a common machine on solid-liquid separation, has advantages of low cost, high solid content and outstanding efficiency that has been widely used in various industries. years, the washing functionof MFP has also been attracting attention for use in the titanium dioxide, sugar,pigment and electrolytic manganese metal In recent years, the washing functionof MFP has also been attracting attention for use in the titanium dioxide, sugar, pigment and electrolytic manganese metal industries[1b14]. LIU et al[14] recovered 50%of water-soluble manganese from an electrolytic manganese residue fEMR) via a MFP using water. -based water washing technology could be industrially applied because it solves the problem of ''water swelling". swelling", which commonly occurs in previous water washing technologies [1 4, 1 5]. On the basis of the previous work of LIU et al [1 4], we attempted to wash the EMR via a MFP using anolyte. In 2009, the MFP-based technology on the leaching and recovery of manganese from EMR via a combination of anolyte washing with water was developed. combination of anolyte washing with water washing was realized and resulted in a patent application being submitted (No. CN1 024700A) 『1 61.Note that However, the possibility of using this technology in the hydrometallurgical zinc production process has not yet been demonstrated. However, the possibility of using this technology in the hydrometallurgical zinc process has never been investigated previously. The thickening, pulping, second leaching, washing, filtering and pressing would be integrated and realised using a single MFR In addition, the leaching of zinc from ZLR In addition, the leaching of zinc from ZLR in the form of spent electrolyte washing would be performed under constant acid concentration via a continuous flow of spent electrolyte. Hencethe feasibility of leaching and recovery of zinc from ZLR would be improved. feasibility of leaching and recovery of zinc from lcaching residue of zinc calcine based on MFP was investigated, combining spent electrolyte washing with flesh water washing. For this work, the uniformity of filter cakes, which is directly related to the leaching result, was examined. Based on this experimental result, the 1eaching and washing on extracting zinc from ZLR were subsequently studied.
1 Introduction
Zinc sulfide ores are the main source of zmc metal in the world, in which zinc generally exists in forms of sphalerite and marmatite. Currently,more than 80 per cent of the zinc is produced by conventional zinc hydrometallurgical methods, including roasting, leaching and electrowinning processes [1, 2]. % of the zinc is produced by conventional zinc hydrometallurgical methods, including roasting, leaching and electrowinning processes [1, 2]. During the roasting process, ZnS is converted to ZnO, but a significant fraction of ZnO reacts with the iron impurities to form zinc ferrite [3-51]. Zinc ferrite is insoluble in mild acidic conditions, strong Hs. A considerable amount of leaching residue will be produced in the subsequent leaching process [f6, 7]. In addition, the leaching reaction rate decreases over time due to the decreasing acid concentration during the tradifional leaching process in the stirred tank. Consequently, incomplete leaching will OCCur, thereby further increasing the generation of zinc leaching residue (ZLR), leading to a significant waste of resources and a high environmental impact. Consequently, incomplete leaching will OCCur, thereby further increasing the generation of zinc leaching residue (ZLR), leading to a significant waste of resources and a high environmental risk [8, 9]. The high demand for zinc has attracted the interest of industry to utilise the ZLR as a valuable secondary source [1].Hydrometallurgical processes are dely applied to recycle zinc from ZLR due to their significant advantages of lower capital and operating costs, as well as being less harmful to the environment [1, 1]. environment [1, 2]. Currently, the most common hydrometallurgical process is to recover zinc from ZLR in a bath of hot concentrated sulfuric acid [10]. high extraction rate of zinc can be obtained using this process, but incomplete leaching still occurs due to the leaching in the stirred tank.Moreover, the hot concentrated acid leaching process involves a high extraction rate of zinc in a bath of hot concentrated sulfuric acid. Moreover, the hot concentrated acid leaching process involves a long reaction time f4-6¨and consumes an enormous amount of energy and sulfuric acid More importantly, in most electrolytic zinc plants, the ZLRs containing water-soluble zinc with a content of less than 5 per cent of the ZLRs were used to produce the ZLRs in the stirred tank. More importantly,in most electrolytic zinc plants, the ZLRs containing water-soluble zinc with a content of less than 5% are directly discharged or heaped, causing a portion of the zinc losses. The water-soluble zinc can cause soil contamination, water pollution and several other serious environmental pollution through the leachate by rainfall [8, 9]. Therefore, finding a cost effective and environment friendly process to recover zinc from ZLR remains a major challenge. The membrane filter press (MFP), which is a common machine on solid. The membrane filter press (MFP), which is a common machine on solid-liquid separation, has advantages of low cost, high solid content and outstanding efficiency that has been widely used in various industries. years, the washing functionof MFP has also been attracting attention for use in the titanium dioxide, sugar,pigment and electrolytic manganese metal In recent years, the washing functionof MFP has also been attracting attention for use in the titanium dioxide, sugar, pigment and electrolytic manganese metal industries[1b14]. LIU et al[14] recovered 50%of water-soluble manganese from an electrolytic manganese residue fEMR) via a MFP using water. -based water washing technology could be industrially applied because it solves the problem of ''water swelling". swelling", which commonly occurs in previous water washing technologies [1 4, 1 5]. On the basis of the previous work of LIU et al [1 4], we attempted to wash the EMR via a MFP using anolyte. In 2009, the MFP-based technology on the leaching and recovery of manganese from EMR via a combination of anolyte washing with water was developed. combination of anolyte washing with water washing was realized and resulted in a patent application being submitted (No. CN1 024700A) 『1 61.Note that However, the possibility of using this technology in the hydrometallurgical zinc production process has not yet been demonstrated. However, the possibility of using this technology in the hydrometallurgical zinc process has never been investigated previously. The thickening, pulping, second leaching, washing, filtering and pressing would be integrated and realised using a single MFR In addition, the leaching of zinc from ZLR In addition, the leaching of zinc from ZLR in the form of spent electrolyte washing would be performed under constant acid concentration via a continuous flow of spent electrolyte. Hencethe feasibility of leaching and recovery of zinc from ZLR would be improved. feasibility of leaching and recovery of zinc from lcaching residue of zinc calcine based on MFP was investigated, combining spent electrolyte washing with flesh water washing. For this work, the uniformity of filter cakes, which is directly related to the leaching result, was examined. Based on this experimental result, the 1eaching and washing on extracting zinc from ZLR were subsequently studied.

2 Experimental 623
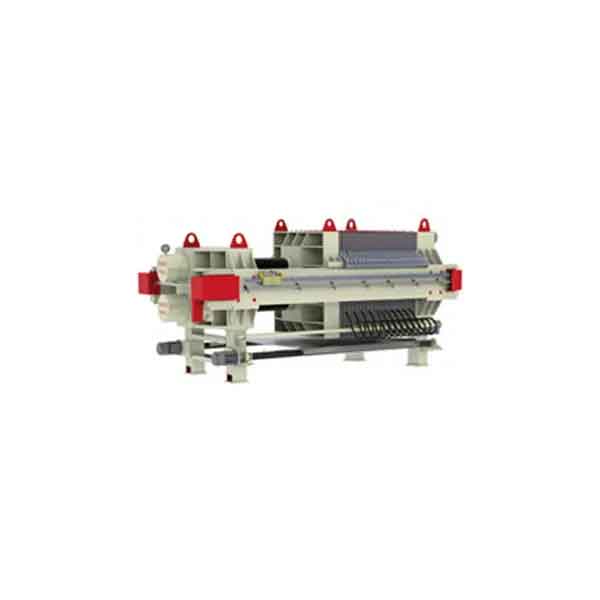
2.1 Materials The experimental study was performed using zinc calcine with a composition of 57% zinc, which was purchased from Hunan Province, China. Spent electrolyte containing 1 60 g/L of H2S04 and 50 g/L of Zn" was used in all of the leaching experiments. under all examined conditions. Under all examined conditions, the zinc concentration was determined based on GB/T 14353.3-2010『17〕, and the hydrogen ion concen仃ation fH+, was measured based on GB 6498.2-2001『181. The membrane filter press (KM470) was from Beijing ZSC Solid-Liquid Separating Technology Co. The membrane filter press (KM470) was from Beijing ZSC Solid-Liquid Separation Technology Co.)
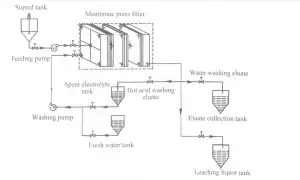
2.2 Experimental procedure The diagram of leaching and recovery of zinc from zinc calcine is presented in Fig. 1.111e proper production process is described briefly as follows. described briefly as follows.1 1 leaching in stirred.tank reactor: Spent electrolyte or sulfuric acid was added to the crashed zinc calcine to leach zinc ions from the ores and to obtain the ZnS04-containing zinc. ions from the ores and to obtain the ZnS04-contained slurry. 2. filtration: the ZnS04-contained slurry was pumped into MFP through central feeding hole and filter pressed to obtain the filter. The ZnS04-contained slurry was pumped into MFP through central feeding hole and filter pressed to obtain the filter cakes (i.e., ZLR); next, the filtrate (1eaching liquor) entered the subsequent production process. 3. 1eaching in Ⅳ[FP: Spent electrolyte at the desired temperature was pumped into the MFP and reacted with filter cakes to leach zinc again and simultaneously recover part of ZnS04. 4) water washing: The filter cakes were washed again with flesh water to further recover ZnS04. 5) pressing: Water with a pressure of 1.5 mL was used for the treatment. with a pressureThe eluate obtained from spent electrolyte washing and flesh water washing steps was then pumped into the membrane plates, which was maintained for 20 min to reduce the water content of filter cakes, and the pressed filter cakes were subsequently discharged from the MFP and transported to landfills. The eluate obtained from spent electrolyte washing and flesh water washing steps were collected and returned to spent electrolyte tank and eluate collection tank. The eluate obtained from spent electrolyte washing and flesh water washing steps were collected and returned to spent electrolyte tank and eluate collection tank, respectively.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Filter cake formation To obtain a high zinc ex仃action rate and recovery rate using an MFP.the most important step is to obtain uniform filter cakes.the particle size of zinc calcine and sedimentation time.which are directly involved with the width of the filter chambers. particle size of zinc calcine and sedimentation time, which are directly involved with the width of the filter chambers, are the most important parameters regarding the uniformity of filter cake. The particle size of zinc calcine and sedimentation time, which are directly involved with the width of the filter chambers, are the most important parameters regarding the uniformity of filter cake. The five-spot test (upper left, bottom left, centre,upper right, bottom right) was used for estimating the uniformity of the filter cakes by measuring the zinc content. The five-spot test (upper left bottom left, centre, upper right, bottom right) was used for estimating the uniformity of the filter cakes by measuring the zinc content and thickness of the cakes at these selected points. Through observation of the filter cakes formed in the MFP, it is found that triangle cakes were easily formed using raw zinc calcine. The presence of zinc calcine of large particle size inhibits the formation of uniform cakes due to its good The presence zinc calcine of large particle size inhibits the formation of uniform cakes due to its good settleability: thus, small size particles should be selected.Choosing the particle size of zinc calcine less than 106 gm仃,able 1 1. which could be obtained in actual production, a series of experiments regarding the filter cake formation were conducted. and the results are presented in Fig.2. From Fig.2.2, using zinc calcines with particle sizes less than 1 06 gm, the zinc content and filter cake thickness vary clearly at the five tested points when the When the filter chamber width is 40 mln, suggesting that the cake uniformity is poor under this condition, which might be due to long sedimentation time. When the filter chamber width is 30 lnnl, the cake uniformity is improved significantly relative to the chamber width of 40 nun. When the filter chamber width is 20 mm, the cake uniformity is improved significantly. When the filter chamber width is 20 mm, the cake uniformity is similar to the results obtained as the chamber width is 30 mm. Thus. it can be clearly observed that the uniforlTl filter cakes could be formed by choosing the particle size of zinc calcine to be less than 1 06 Bm for filter chamber widths of 20 mm and 30 mill. As a result, the zinc calcines with particle size 1ess than 1 06 Bm were used in the following filter chamber. As a result, the zinc calcines with particle size 1ess than 1 06 Bm were used in the following experiments. The processing capacity of MFP with 20 mm width chamber is 10wer than that with 30 toni width chamber. The processing capacity of MFP with 20 mm width chamber is 10wer than that with 30 toni width chamber.Therefore. combining the results of processing capacity and cake uniformity,the chamber width of 30 finn was selected in the following The chamber width of 30 finn was selected in the following experiments.
3.2 Leaching of zinc from zinc calcine In this lcaching process, 1 00 L of spent electrolyte solution was added to a 300 L stainless steel drum equipped with a variable speed stirrer and then stirred for approximately 1 h at a speed of 60 r/min. Next, the 1eaching solution was adjusted by adding zinc calcine or Next, the 1eaching solution was adjusted by adding zinc calcine or sulfate acid until the final Zn "concentration of electrolyte was in the range of 130-140 g/L and the final H2S04 concentration was in the range of l-2 g/L. Subsequently, the ZnS04-contained slurry was filtered using a MFE The analysis results of zinc calcine and ZLR are presented in 1 'ables 2 and 3. The analysis results of zinc calcine and ZLR are presented in 1, 2 and 3, respectively. As presented in Table 2, the grade of zinc calcine is 57.52%, in which ZnO approximately accounts for 90.06% of total zinc in mass. Table 3 indicates that in this process of leaching, most of the Zn0 is converted to ZnS04, resulting in the dramatic decrease of the content of ZnO. Table 3 indicates that in this process of leaching most of the Zn0 is converted to ZnS04, resulting in the dramatic decrease of the content of ZnO. After solid-liquid separation using the MFP, many insoluble materials are concentrated in the residue. leaching residue is higher than 20%, causing the extraction rate of zinc in this process to be less than 90%. Analysis of ZLR indicates that zinc iS mainly presented in the forills of ZnO. presented in the forills of ZnFe204, ZnO and ZnS04, which in total account for uD to 80% of the zinc iS.(Thus, a secondary leaching process is required to recover the remaining zinc.
3.3 Leaching of zinc from ZLR In this leaching process, the zinc was extracted from ZLR obtained in Section 3.2 in the form of spent electrolyte washing To dissolve ZnFe204 using MFE, strict leaching conditions, such as high temperature (above 90°C, and high concentration of acid solution (100 -200 g/L), were applied. -Under hi. temperature and high acid concentration conditions, the extraction rate of zinc can increase to approximately 97% [19, 20]. approximately 97% [19, 20]. To enable a comparison with the extraction rate obtained in the traditional route, the lcaching conditions in the present work are under a temperature in the range of 0.5 to 0.5°C. The extraction rate of zinc was determined as follows The lcaching conditions in the present work are under a temperature in the range of 90 to 96 oC and an acid concentration in the range of 1 00 to 200 g/L. Becanse alsoe leaching residues of zinc calcine Becanse also e leaching residues of zinc calcine were fixed in the chamber of the MFP. the high reaction temperature condition was realized through heating of the spent electrolyte. Figure 3 shows the Zn "and H2S04 concentrations with the MFP. Figure 3 shows the Zn "and H2S04 concentrations with leaching time under atemperature in the range of 90 to 96 oC during the leaching process based on MFE From Fig. 3, the Zn "concentration is the highest in the chamber. The Zn "concentration is observed to obviously increase during the initial 5 min, followed by a decrease to 55 gui after washing for 60 min and only a slight change around the level of 55 g/L in the following 30 min. Conversely'the H2S04 concentration obviously decreases during the initial 5 min. followed by a decrease to 55 g/L in the following 30 min. Conversely'the H2S04 concentration obviously decreases during the initial 5 min. followed by an increase to 11 7 g/L after washing for 60 min and then slight changes around the level of 120 g/L in next 30 min. Based on these Based on these above results, it can be concluded that the violently reaction of the leaching residue with the hot spent electrolyte only lasts for approximately 60 min. The analysis result of the residue after hot concentrated acid leaching for 90 min is presented in T2lble 4. Clearlv. the zinc content in the residue reduces significantly from over 20% (Table 3) to less than 1 0% (Table 41. As a consequence, the zinc extraction rate 1ncreases to 97%. This result obviously demonstrates that using a MFP as a leaching reactor could not only ensure a high extraction rate but also reduce the leaching time compared with the traditional hot concentrated acid The short leaching time using a MFP might be due to the constant reaction conditions of high temperature and high acid concentration during the whole process when using a MFE Based on the above results. The short leaching time using a MFP might be due to the constant reaction conditions of high temperature and high acid concentration during the whole process when using a MFE Based on the above results. temperatures, such as at 30 oC, 60 to 70 oC, 70 to 80 oC and 80 to 90 oC. to reduce the energy consumption further. The zinc extraction rate at 30 oC is 92.67% and increases to 94.95% at 60 to 70 oC. When the 1eaching temperature is further increased to 80 to 90 oC, the ex仃action ratio increases to 94.95% at 60 to 70 oC. The ex仃action ratio increases to 95.56%. The temperature of spent electrolyte has an obvious effect on t11e zinc extraction ratio. high zinc extraction could be obtained by increasing the temperature of the electrolyte. High zinc extraction could be obtained by increasing the temperature of leaching, which is consistent wim the results of Ref.f191. Under Iow temperatures, the energy consumption is lower,the extraction ratio can be increased by 1.5 per cent. Under Iow temperatures, the energy consumption is lower,the extraction ratio can not reach the traditional result of 97%.In conelusion, the hot acid leaching only at 90 to 96 oC or above can achieve the ideal result(i). achieve the ideal result(i.e., more than 97%,...).
3.4 Recovery of water-soluble zinc
The water-soluble zinc approximately accounts for 3%of the total zinc in the residue after hot acidTo recover this part of the zinc, the leaching residue was further washed with Water. Figure 5 shows that both the Zn2+and H,S04 concentrations of eluate decrease with increasing washing time. Figure 5 shows that both the Zn2+and H,S04 concentrations of eluate decrease with increasing washing time.especially in the initial 5 min. These results indicate that Zn "and H,S04 These results indicate that Zn "and H,S04 in the zinc residue could be quickly washed out by Water using the MFP. After washing for 25 min, the final Znz+and H2S04 concentrations of eluate decrease to 0.05 ki and H2S04 concentrations of eluate. to 0.05 g/l and 1.25 g/l.pectively. The final residue obtained after being washed and pressed merely contains 6% of zinc. in which the water-soluble zinc only accounts for 0.07% (Table 5), suggesting that the majority of water-soluble zinc is recovered during the water washing process. Compared with the traditional hot concentrated acid leaching process, the water-soluble zinc lost in the leaching residue iS very 10 %. The water-soluble zinc lost in the leaching residue iS very 10W. 3.5 Washing uniformity To estimate the washing results, the washing uniformity of MFP was examined by measuring.Both the total zinc and the water-soluble zinc were measured. Both the total zinc and the water-soluble zinc contents in the final residue. As presented in Rlble 6. change slightly at five selected points (upper left, bottom left, centre,upper right, and bottom right) in the residue, indicating that the hot spent The zinc that can be extracted in zinc calcine and the Water-soluble zinc that can be recovered in the residue are completely uniforiil. The zinc that can be extracted in zinc calcine and the Water-soluble zinc that can be recovered in the residue are completely extracted and recovered by USing the MFP.
4 Conclusions
1] The use of a MFP is found to be completely feasible and effective to 1each and recover zinc from leaching residues ofzinc calcine.
2] The zinc calcines with particle size of less than 1 06 gm and MFP chambers with a width of 30 I/IlTI are proper for establishing unifornl filter cakes to obtain acceptable leaching and recovery results.
2 Experimental 623
2.1 Materials The experimental study was performed using zinc calcine with a composition of 57% zinc, which was purchased from Hunan Province, China. Spent electrolyte containing 1 60 g/L of H2S04 and 50 g/L of Zn" was used in all of the leaching experiments. under all examined conditions. Under all examined conditions, the zinc concentration was determined based on GB/T 14353.3-2010『17〕, and the hydrogen ion concen仃ation fH+, was measured based on GB 6498.2-2001『181. The membrane filter press (KM470) was from Beijing ZSC Solid-Liquid Separating Technology Co. The membrane filter press (KM470) was from Beijing ZSC Solid-Liquid Separation Technology Co.)
2.2 Experimental procedure The diagram of leaching and recovery of zinc from zinc calcine is presented in Fig. 1.111e proper production process is described briefly as follows. described briefly as follows.1 1 leaching in stirred.tank reactor: Spent electrolyte or sulfuric acid was added to the crashed zinc calcine to leach zinc ions from the ores and to obtain the ZnS04-containing zinc. ions from the ores and to obtain the ZnS04-contained slurry. 2. filtration: the ZnS04-contained slurry was pumped into MFP through central feeding hole and filter pressed to obtain the filter. The ZnS04-contained slurry was pumped into MFP through central feeding hole and filter pressed to obtain the filter cakes (i.e., ZLR); next, the filtrate (1eaching liquor) entered the subsequent production process. 3. 1eaching in Ⅳ[FP: Spent electrolyte at the desired temperature was pumped into the MFP and reacted with filter cakes to leach zinc again and simultaneously recover part of ZnS04. 4) water washing: The filter cakes were washed again with flesh water to further recover ZnS04. 5) pressing: Water with a pressure of 1.5 mL was used for the treatment. with a pressureThe eluate obtained from spent electrolyte washing and flesh water washing steps was then pumped into the membrane plates, which was maintained for 20 min to reduce the water content of filter cakes, and the pressed filter cakes were subsequently discharged from the MFP and transported to landfills. The eluate obtained from spent electrolyte washing and flesh water washing steps were collected and returned to spent electrolyte tank and eluate collection tank. The eluate obtained from spent electrolyte washing and flesh water washing steps were collected and returned to spent electrolyte tank and eluate collection tank, respectively.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Filter cake formation To obtain a high zinc ex仃action rate and recovery rate using an MFP.the most important step is to obtain uniform filter cakes.the particle size of zinc calcine and sedimentation time.which are directly involved with the width of the filter chambers. particle size of zinc calcine and sedimentation time, which are directly involved with the width of the filter chambers, are the most important parameters regarding the uniformity of filter cake. The particle size of zinc calcine and sedimentation time, which are directly involved with the width of the filter chambers, are the most important parameters regarding the uniformity of filter cake. The five-spot test (upper left, bottom left, centre,upper right, bottom right) was used for estimating the uniformity of the filter cakes by measuring the zinc content. The five-spot test (upper left bottom left, centre, upper right, bottom right) was used for estimating the uniformity of the filter cakes by measuring the zinc content and thickness of the cakes at these selected points. Through observation of the filter cakes formed in the MFP, it is found that triangle cakes were easily formed using raw zinc calcine. The presence of zinc calcine of large particle size inhibits the formation of uniform cakes due to its good The presence zinc calcine of large particle size inhibits the formation of uniform cakes due to its good settleability: thus, small size particles should be selected.Choosing the particle size of zinc calcine less than 106 gm仃,able 1 1. which could be obtained in actual production, a series of experiments regarding the filter cake formation were conducted. and the results are presented in Fig.2. From Fig.2.2, using zinc calcines with particle sizes less than 1 06 gm, the zinc content and filter cake thickness vary clearly at the five tested points when the When the filter chamber width is 40 mln, suggesting that the cake uniformity is poor under this condition, which might be due to long sedimentation time. When the filter chamber width is 30 lnnl, the cake uniformity is improved significantly relative to the chamber width of 40 nun. When the filter chamber width is 20 mm, the cake uniformity is improved significantly. When the filter chamber width is 20 mm, the cake uniformity is similar to the results obtained as the chamber width is 30 mm. Thus. it can be clearly observed that the uniforlTl filter cakes could be formed by choosing the particle size of zinc calcine to be less than 1 06 Bm for filter chamber widths of 20 mm and 30 mill. As a result, the zinc calcines with particle size 1ess than 1 06 Bm were used in the following filter chamber. As a result, the zinc calcines with particle size 1ess than 1 06 Bm were used in the following experiments. The processing capacity of MFP with 20 mm width chamber is 10wer than that with 30 toni width chamber. The processing capacity of MFP with 20 mm width chamber is 10wer than that with 30 toni width chamber.Therefore. combining the results of processing capacity and cake uniformity,the chamber width of 30 finn was selected in the following The chamber width of 30 finn was selected in the following experiments.
3.2 Leaching of zinc from zinc calcine In this lcaching process, 1 00 L of spent electrolyte solution was added to a 300 L stainless steel drum equipped with a variable speed stirrer and then stirred for approximately 1 h at a speed of 60 r/min. Next, the 1eaching solution was adjusted by adding zinc calcine or Next, the 1eaching solution was adjusted by adding zinc calcine or sulfate acid until the final Zn "concentration of electrolyte was in the range of 130-140 g/L and the final H2S04 concentration was in the range of l-2 g/L. Subsequently, the ZnS04-contained slurry was filtered using a MFE The analysis results of zinc calcine and ZLR are presented in 1 'ables 2 and 3. The analysis results of zinc calcine and ZLR are presented in 1, 2 and 3, respectively. As presented in Table 2, the grade of zinc calcine is 57.52%, in which ZnO approximately accounts for 90.06% of total zinc in mass. Table 3 indicates that in this process of leaching, most of the Zn0 is converted to ZnS04, resulting in the dramatic decrease of the content of ZnO. Table 3 indicates that in this process of leaching most of the Zn0 is converted to ZnS04, resulting in the dramatic decrease of the content of ZnO. After solid-liquid separation using the MFP, many insoluble materials are concentrated in the residue. leaching residue is higher than 20%, causing the extraction rate of zinc in this process to be less than 90%. Analysis of ZLR indicates that zinc iS mainly presented in the forills of ZnO. presented in the forills of ZnFe204, ZnO and ZnS04, which in total account for uD to 80% of the zinc iS.(Thus, a secondary leaching process is required to recover the remaining zinc.
3.3 Leaching of zinc from ZLR In this leaching process, the zinc was extracted from ZLR obtained in Section 3.2 in the form of spent electrolyte washing To dissolve ZnFe204 using MFE, strict leaching conditions, such as high temperature (above 90°C, and high concentration of acid solution (100 -200 g/L), were applied. -Under hi. temperature and high acid concentration conditions, the extraction rate of zinc can increase to approximately 97% [19, 20]. approximately 97% [19, 20]. To enable a comparison with the extraction rate obtained in the traditional route, the lcaching conditions in the present work are under a temperature in the range of 0.5 to 0.5°C. The extraction rate of zinc was determined as follows The lcaching conditions in the present work are under a temperature in the range of 90 to 96 oC and an acid concentration in the range of 1 00 to 200 g/L. Becanse alsoe leaching residues of zinc calcine Becanse also e leaching residues of zinc calcine were fixed in the chamber of the MFP. the high reaction temperature condition was realized through heating of the spent electrolyte. Figure 3 shows the Zn "and H2S04 concentrations with the MFP. Figure 3 shows the Zn "and H2S04 concentrations with leaching time under atemperature in the range of 90 to 96 oC during the leaching process based on MFE From Fig. 3, the Zn "concentration is the highest in the chamber. The Zn "concentration is observed to obviously increase during the initial 5 min, followed by a decrease to 55 gui after washing for 60 min and only a slight change around the level of 55 g/L in the following 30 min. Conversely'the H2S04 concentration obviously decreases during the initial 5 min. followed by a decrease to 55 g/L in the following 30 min. Conversely'the H2S04 concentration obviously decreases during the initial 5 min. followed by an increase to 11 7 g/L after washing for 60 min and then slight changes around the level of 120 g/L in next 30 min. Based on these Based on these above results, it can be concluded that the violently reaction of the leaching residue with the hot spent electrolyte only lasts for approximately 60 min. The analysis result of the residue after hot concentrated acid leaching for 90 min is presented in T2lble 4. Clearlv. the zinc content in the residue reduces significantly from over 20% (Table 3) to less than 1 0% (Table 41. As a consequence, the zinc extraction rate 1ncreases to 97%. This result obviously demonstrates that using a MFP as a leaching reactor could not only ensure a high extraction rate but also reduce the leaching time compared with the traditional hot concentrated acid The short leaching time using a MFP might be due to the constant reaction conditions of high temperature and high acid concentration during the whole process when using a MFE Based on the above results. The short leaching time using a MFP might be due to the constant reaction conditions of high temperature and high acid concentration during the whole process when using a MFE Based on the above results. temperatures, such as at 30 oC, 60 to 70 oC, 70 to 80 oC and 80 to 90 oC. to reduce the energy consumption further. The zinc extraction rate at 30 oC is 92.67% and increases to 94.95% at 60 to 70 oC. When the 1eaching temperature is further increased to 80 to 90 oC, the ex仃action ratio increases to 94.95% at 60 to 70 oC. The ex仃action ratio increases to 95.56%. The temperature of spent electrolyte has an obvious effect on t11e zinc extraction ratio. high zinc extraction could be obtained by increasing the temperature of the electrolyte. High zinc extraction could be obtained by increasing the temperature of leaching, which is consistent wim the results of Ref.f191. Under Iow temperatures, the energy consumption is lower,the extraction ratio can be increased by 1.5 per cent. Under Iow temperatures, the energy consumption is lower,the extraction ratio can not reach the traditional result of 97%.In conelusion, the hot acid leaching only at 90 to 96 oC or above can achieve the ideal result(i). achieve the ideal result(i.e., more than 97%,...).
3.4 Recovery of water-soluble zinc
The water-soluble zinc approximately accounts for 3%of the total zinc in the residue after hot acidTo recover this part of the zinc, the leaching residue was further washed with Water. Figure 5 shows that both the Zn2+and H,S04 concentrations of eluate decrease with increasing washing time. Figure 5 shows that both the Zn2+and H,S04 concentrations of eluate decrease with increasing washing time.especially in the initial 5 min. These results indicate that Zn "and H,S04 These results indicate that Zn "and H,S04 in the zinc residue could be quickly washed out by Water using the MFP. After washing for 25 min, the final Znz+and H2S04 concentrations of eluate decrease to 0.05 ki and H2S04 concentrations of eluate. to 0.05 g/l and 1.25 g/l.pectively. The final residue obtained after being washed and pressed merely contains 6% of zinc. in which the water-soluble zinc only accounts for 0.07% (Table 5), suggesting that the majority of water-soluble zinc is recovered during the water washing process. Compared with the traditional hot concentrated acid leaching process, the water-soluble zinc lost in the leaching residue iS very 10 %. The water-soluble zinc lost in the leaching residue iS very 10W. 3.5 Washing uniformity To estimate the washing results, the washing uniformity of MFP was examined by measuring.Both the total zinc and the water-soluble zinc were measured. Both the total zinc and the water-soluble zinc contents in the final residue. As presented in Rlble 6. change slightly at five selected points (upper left, bottom left, centre,upper right, and bottom right) in the residue, indicating that the hot spent The zinc that can be extracted in zinc calcine and the Water-soluble zinc that can be recovered in the residue are completely uniforiil. The zinc that can be extracted in zinc calcine and the Water-soluble zinc that can be recovered in the residue are completely extracted and recovered by USing the MFP.
4 Conclusions
1] The use of a MFP is found to be completely feasible and effective to 1each and recover zinc from leaching residues ofzinc calcine.
2] The zinc calcines with particle size of less than 1 06 gm and MFP chambers with a width of 30 I/IlTI are proper for establishing unifornl filter cakes to obtain acceptable leaching and recovery results.
 Plate and frame chamber diaphragm filter presses
Plate and frame chamber diaphragm filter presses


